normal lv end diastolic volume|end diastolic volume calculation : 2024-10-04 Normal 2D measurements from the apical 4-chamber view: RV medio-lateral end-diastolic dimension ≤ 4.3 cm, RV end-diastolic area ≤ 35.5 cm 2, maximal RA medio-lateral and supero-inferior dimensions ≤ . [Question] I’ve completed all of the MSQ as a Black Mage and have just started grinding my relic weapon, yet still haven’t found my class gear. In the previous expansions, it was a set of armor you got from the npc who gave out class quests at max level. Did they do away with class gear, or is it something different this time?
0 · what increases end diastolic volume
1 · normal Lv end diastolic dimension
2 · left ventricular end diastolic volume
3 · end diastolic volume normal range
4 · end diastolic volume chart
5 · end diastolic volume calculation
6 · end diastolic index ml m2
7 · Lv diastolic volume normal range
Failiem.lv glabāšanas platforma piedāvā visaptverošus risinājumus visa veida satura - dokumentu, foto, video, mūzikas, lietojumprogrammu, grāmatu glabāšanai, kopīgošanai, publicēšanai un pat pārdošanai. Ērti glabā, dalies vai pārdod foto, video un citu saturu. Ātri pārsūti lielu failu oriģinālus.
normal lv end diastolic volume*******Left ventricular end-diastolic volume is one of several calculations that doctors use to determine how well the heart is pumping. This calculation, . See more End-diastolic volume is the amount of blood that is in the ventricles before the heart contracts. Doctors use end-diastolic volume .end diastolic volume calculation End-diastolic volume is the amount of blood that is in the ventricles before the heart contracts. Doctors use end-diastolic volume . Normal 2D measurements from the apical 4-chamber view: RV medio-lateral end-diastolic dimension ≤ 4.3 cm, RV end-diastolic area ≤ 35.5 cm 2, maximal RA medio-lateral and supero-inferior dimensions ≤ . LVM = left ventricular mass, BSA = body surface area, EDV = end-diastolic volume. Figure 3. The normal age variation in left ventricular parameters in males (left) .Determining the left ventricular (LV) end-diastolic volume index (EDVI) is essential to evaluating LV function. LV EDVI—the volume of blood in the LV at end load filling indexed for body surface area (ml/m 2 )—may be .In cardiovascular physiology, end-diastolic volume (EDV) is the volume of blood in the right or left ventricle at end of filling in diastole which is amount of blood present in .Results: The normal ranges for LV end-diastolic volume measurements after adjustment to body surface area (BSA) were 62-120 ml for males and 58-103 ml for females. LV mass .
LV Volume = [7/ (2.4 + LVID)] * LVID3. RWMA, either close or distant, may cause the volume analysis to be incorrect. If the endocardial boarder is poorly seen, then the area .The maximal pressure that can be developed by the ventricle at any left ventricular volume is defined by the end-systolic pressure-volume relationship (ESPVR), which represents . diastolic dysfunction = disorder of LV filling where LV is unable to fill to a normal LVEDV without an increase in end-diastolic pressure. m-mode ‘slow relaxation’ in motion of the anterior mitral valve .
Normal (reference) values for echocardiography, for all measurements, according to AHA, ACC and ESC, with calculators, reviews and e-book. . (typically >30% thickening from end-diastole to end-systole). 1: . LV .
1. Introduction. Left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction (EF) and LV end-diastolic and end-systolic volumes (LVEDV and LVESV, respectively) are commonly used as clinical parameters reflecting global LV systolic performance or LV remodeling [1, 2].Of note, compared with LVEF or LVEDV, previous reports emphasized the superiority of .
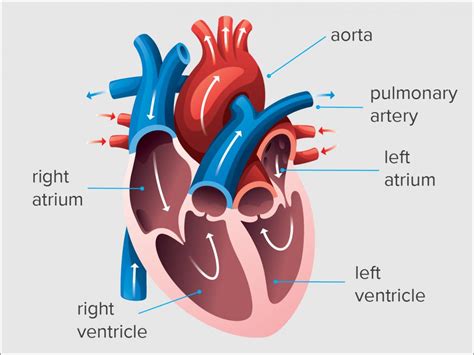
Point 1 on the PV loop is the pressure and volume at the end of ventricular filling (diastole) and therefore represents the end-diastolic pressure and end-diastolic volume (EDV) for the ventricle. As the ventricle begins to contract isovolumetrically (phase b), the mitral valve closes and the LVP increases, but the LV volume remains the same, therefore resulting .
The LV end-diastolic volume (EDV) . For example, chronic volume overload can shift the ventricular diastolic pressure-relation rightward so that volume is increased at a normal end-diastolic pressure, whereas chronic pressure overload can shift the diastolic P-V relation leftward and for the same end-diastolic pressure, result in a smaller . Yet, one type of HF is characterized by near-normal values for LV end-diastolic volume (EDV) and even a smaller end-systolic volume (ESV) than in matched groups of persons without cardiac disease. Furthermore, accumulating evidence indicates that, both in terms of shape and size, in men and women, the heart reacts differently to . Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is the central measure of left ventricular systolic function. LVEF is the fraction of chamber volume ejected in systole (stroke volume) in relation to the volume of the blood in the ventricle at the end of diastole (end-diastolic volume). Stroke volume (SV) is calculated as the difference between . This should suggest severe, irreversible LV dysfunction. By contrast, a patient with the same end-diastolic volume, an EF of 50%, and a regurgitant fraction of 50% would have a ratio of regurgitant volume to end-diastolic volume of 33/130, or 0.25. The higher ratio of 0.25 indicates a potentially reversible phase of chronic MR. Knowledge about age-specific normal values for left ventricular mass (LVM), end-diastolic volume (EDV), end-systolic volume (ESV), stroke volume (SV) and ejection fraction (EF) by cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMR) is of importance to differentiate between health and disease and to assess the severity of disease. The aims of the study .The term LV filling pressures can refer to mean pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP), mean left atrial (LA) pressure (LAP), LV pre-A pressure, mean LV diastolic pressure, and LV end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP). 26,27 In the early stages of diastolic dysfunction, LVEDP is the only abnormally elevated pressure, while mean PCWP and . Impairment of left ventricular (LV) diastolic function is common amongst those with left heart disease and is associated with significant morbidity. Given that, in simple terms, the ventricle can only eject the volume with which it fills and that approximately one half of hospitalisations for heart failure (HF) are in those with .
normal lv end diastolic volume end diastolic volume calculation(see below) and is derived from the LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) and LV end-systolic volume (LVESV). . Normal values for LV chamber dimensions (linear), volumes and ejection fraction vary by gender. A normal ejection fraction is 53-73% (52-72% for men, 54-74% for women).
Cardiologists also use stroke volume when assessing cardiac dysfunction in those with congestive heart failure. The computation of left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) involves dividing the stroke . Results. In the derivation cohort, there was a strong positive relationship between exercise duration and LV end‐diastolic volume deciles (r 2 = 0.85; P < 0.001).Regression analyses of several LV dimensional parameters revealed that the body surface area–based LV end‐diastolic volume index was best suited to predict exercise . Systolic function is conveniently (although not always accurately) measured as the ejection fraction. Diastolic function has been more difficult to evaluate. 1,3 Traditionally, invasive measures of LV diastolic pressure–volume relations and the rate of LV pressure fall during isovolumetric relaxation have been used. However, these . LVEF, defined as the ratio of LV stroke volume to LV end-diastolic volume, is one of the most frequently measured variables in clinical practice. However, LVEF is an imperfect measure of LV contractility, affected also by preload, afterload, heart rate, and LV geometry. . Published normal ranges for LVEF have varied between techniques.normal lv end diastolic volume Those with diastolic heart failure will have signs and symptoms of heart failure as well as LVDD However, those with diastolic heart failure usually have a normal ejection fraction. If LV mass is normal (i.e. the patient does not have LVH), . LVEDV(i), left ventricular end-diastolic volume (indexed); LVESV(i), left ventricular end-systolic volume (indexed). Left ventricular ejection fraction. Summary . Reference intervals for LVEF are the same for males and females (Table 4).

Diastolic function and echocardiographic assessment. The importance of systolic function can be understood on an intuitive basis. Consider the fact that the left ventricle contracts and ejects blood into the aorta roughly 100,000 times daily, each time overcoming the aortic resistance, which is typically 110 mmHg or more.
Ienāc Facebook, lai dalītos un sazinātos ar draugiem, ģimeni un paziņām.
normal lv end diastolic volume|end diastolic volume calculation











